The Magic of PRP Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction

PRP Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction: A Revolutionary Approach Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition affecting millions of men worldwide. Traditional treatments, such as medications and lifestyle changes, have been effective for many, but not all. For those seeking alternative or complementary therapies, Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy is emerging as a promising option. What […]
Understanding STDs

Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are a common concern for sexually active individuals. These infections can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or sexual orientation. While prevention is crucial, knowing when to consult a urologist for STD-related concerns is equally important. In this blog, we will discuss STDs, their symptoms, and […]
Amazing Facts about PRP Treatment For Erectile Dysfunction!
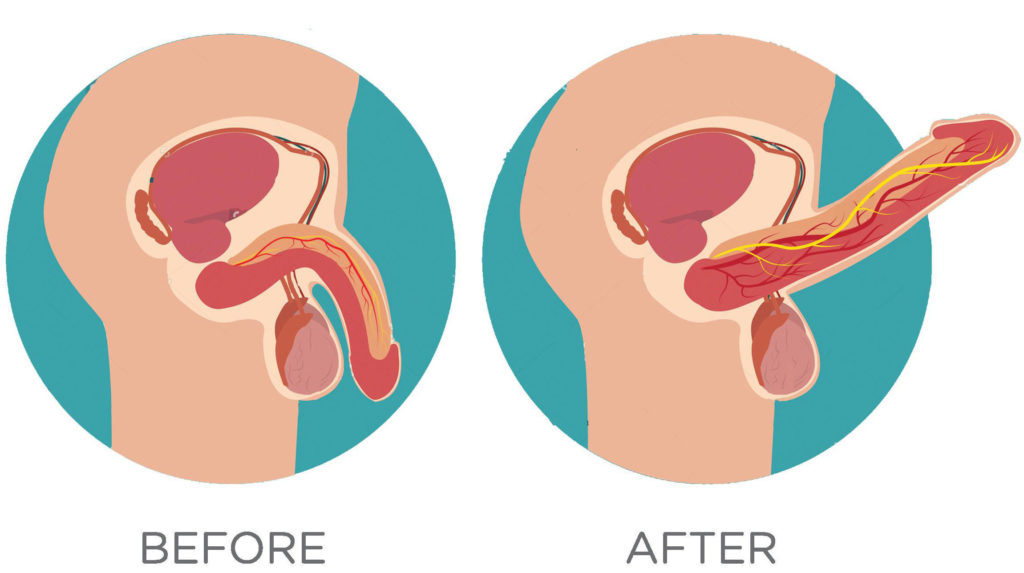
PRP treatment for erectile dysfunction What is PRP? A blood component known as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is supposed to encourage tissue growth and healing. PRP therapy is used to repair muscle or tendon injuries, promote hair growth, and hasten surgical recuperation. Additionally, it is employed as an experimental or different form of treatment for: […]
Hurry up to treat varicoceles!
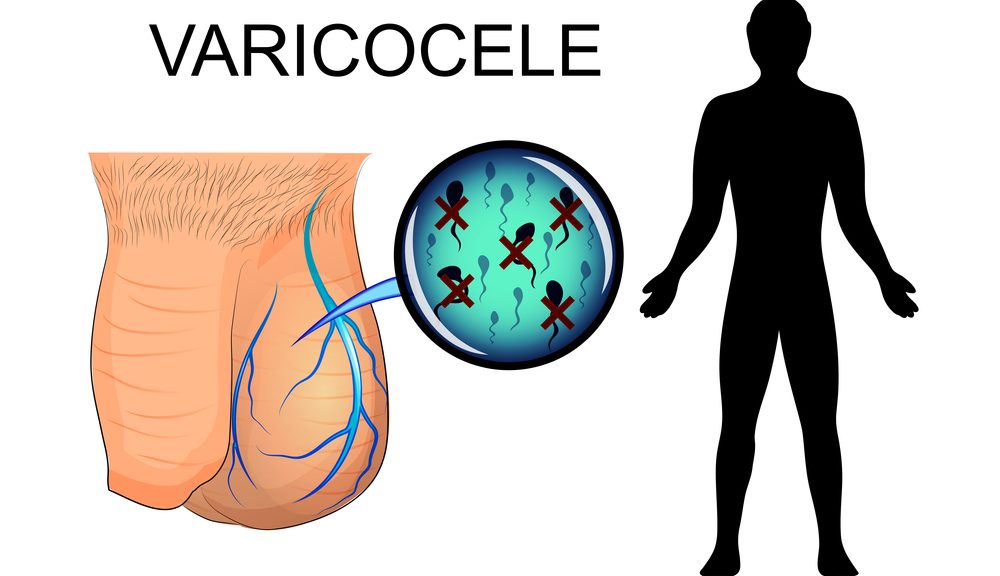
Varicoceles What are varicoceles? Varicoceles are when veins called pampiniform plexus become enlarged inside your scrotum (the sac that protects and holds the testicles). About ten to fifteen males out of one hundred have varicocele; it is like getting a varicose vein in your leg. This condition is most common in young men; and affects […]
Low libido in men

Physical and psychological issues can cause low libido in men; so don’t hesitate to book your appointment at Modern Care Clinic with dr. Fouad Khoury, to continue a normal sexual life and to avoid problems in your relationship. What is low libido in men? Low libido in men describes a decreased interest in sexual activity; […]
Penile Prosthesis the BEST surgical treatment for ED in Lebanon
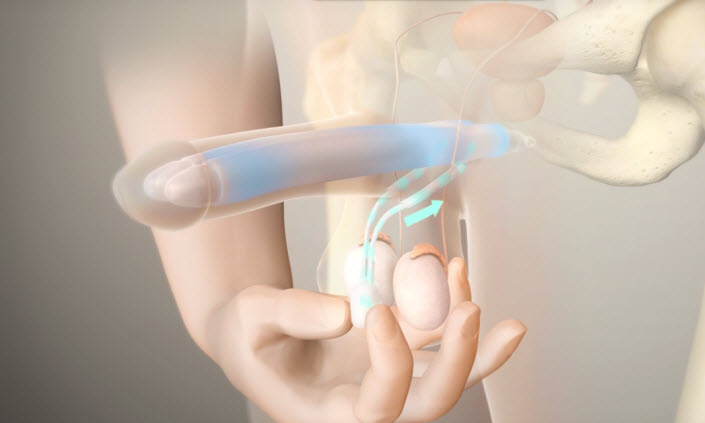
Penile prosthesis Definition A penile prosthesis or Penile Implant is the best surgery that helps men with erectile dysfunctions when other treatments failed. This procedure involves placing a prosthetic device or penile implant inside the penis and scrotum; so the patient can get a sufficient erection for sexual activities. And it lasts for 45 minutes […]
TOGETHER towards a better prognosis with Rezum water vapor!
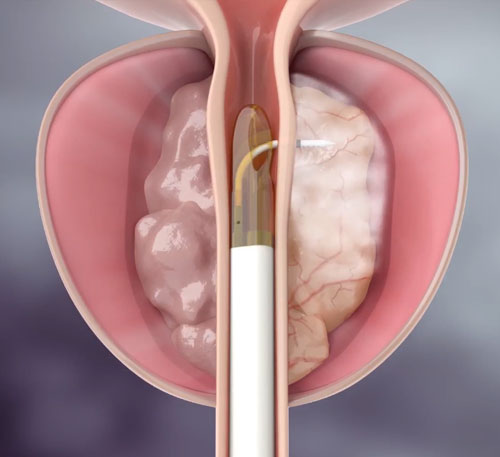
Rezum Water Vapor Rezum water vapor is the best therapy for prostatic hyperplasia. We have a better prognosis with Rezum water vapor. What is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)? BPH is the most common prostate problem in men especially at the age of 50 and over. It is a condition in which the prostate, a gland […]
Sexual Health in Men

Sexual health in men whether Erectile dysfunction or Premature ejaculation can significantly affect his daily life Erectile dysfunction Erectile dysfunction (ED) is when a man (particularly in men over 40) has difficulty to get or keep an erection suitable for sexual relation or any other sexual activity. ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION CAUSES: Physical causes: Common causes include: […]
Sex Scandals in Recent Times
No matter how civilized we become, deep down inside, we are all animals. And, the way we bring forth our animalistic needs is by our sexual instincts. Now, you might think that celebrities and famous personalities won’t have weird sexual kinks and fetishes that a normal human being would have. But, in reality, they are […]
Erectile dysfunction

Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a problem that needs to be diagnosed correctly. Once we find the proper cause, it becomes possible to provide with the correct treatment.
