Maintenance Therapy For Bladder Cancer … What is the role of BCG?
Bladder cancer can come back; for this reason, the patient needs follow-up tests for years after finishing the treatment.
The best follow-up treatment is the BCG: Bacillus Calmette-Guérinthat used since 1920 to attenuated the action of the tubercle bacilli that causes tuberculosis.
The action of BCG
The local immune response is closely linked to the interaction of three systems: the patient, the BCG (Mycobacteria), and the tumor. This interaction will give rise to a cascade of immunological events, some of which will be essential for the protective action of BCG against tumor recurrence and progression. There are three phases in the immune response to BCG. First, the BCG adheres to the urothelium and then is phagocytosed by antigen-presenting cells; this phase corresponds to the early release of inflammatory cytokines. These cytokines could be involved in certain undesirable effects but they could also participate in cytotoxic phenomena. The second phase is the recognition of bacterial antigens by CD4 helper lymphocytes. This cellular activation will lead to the third phase which is the amplification of cytotoxic populations capable of killing tumor cells. All of these cells also produce cytokines that help regulate the immune response.
Indications of BCG:
BCG (powder and solvent for suspension for intravesical use) is used to :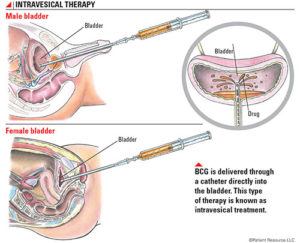
-curative treatment of urothelial carcinoma in situ.
-prophylactic treatment of relapses of urothelial carcinoma limited to the mucosa, no muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma, urothelial carcinoma in situ.
Protocol of injection of BCG:
2-3 weeks after TURBT ( weekly for 6 weeks).
After a cystoscopy: Maintenance therapy consists of 3 treatments at weekly intervals given for a minimum of 1 year
up to 3 years; every 3 months for 2 years, then every 6 months for 2 years, and finally yearly.
What are the side effects of BCG?
It is common for patients to experience flu-like symptoms for 2–3 days after the treatment.
Other side effects include:
-Trouble to empty your bladder.
-Blood in your urine, dark urine.
-Urinary tract infections.
-Pain when you urinate.
-Vomiting, pain in the upper part of the stomach.
-Trouble breathing.
-Fatigue.
-Signs of a penis infection: burning, itching, odor, discharge, pain, tenderness, redness or swelling of the genital or rectal area, fever, not feeling well.
-Yellowing of your skin or eyes.
After the treatment (after 4 to 6 hours), the patient may present bladder symptoms: sudden need to urinate, frequent urination, stomach discomfort, bloating, and possibly loss of bladder control. If these symptoms last for more than 2 days; you should consult your urologist.
Follow the link for more information about BCG.